
WHAT WE DO
OUR WORK
ABOUT US
GET IN TOUCH →
AI Policy
In response to the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies and their increasing integra1on into our company's opera1ons, SPRING Family recognize the importance of establishing clear guidelines for the responsible and effective use of AI and has therefore implemented an Internal AI Usage Policy. The policy serves as a framework to promote ethical AI practices, protect data, ensure transparency, and mi1gate potential risks associated with both non-generative and generative AI within the en1re group.
As AI continues to evolve, the policy provides fundamental principles and considerations that will guide our approach to AI usage, ensuring alignment with our company values and objectives. It is designed to foster innovation while priori1zing the well-being of our clients, employees, and stakeholders.
As AI technology evolves and the business landscape changes, we will periodically review and update the AI Policy to stay in line with best practices and industry standards.
Definitions
Non-generative AI: Explanation and Examples
Non-generative AI, also known as traditional or narrow AI, refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to perform specific, predefined tasks within a limited scope. Unlike generative AI, these systems cannot create new content or generate novel information beyond their training data. Instead, they rely on predefined algorithms and patterns to execute tasks and provide solutions.
Examples of industry-related Non-generative AI:
- Image Recognition: Non-generative AI models can be trained to recognize objects, patterns, or faces in images, making them valuable tools across various applications.
- Recommendation Systems: E-commerce platforms often use non-generative AI to suggest products or content based on user behavior, purchase history, or preferences.
- Speech Recognition: Virtual assistants and voice-controlled devices utilize non-generative AI to convert spoken language into actionable commands.
Generative AI: Explanation and Examples
Generative AI, also referred to as creative AI, involves models capable of generating new content or data that was not present in the original training set. These systems are more versatile and can produce original output based on patterns learned during training. Generative AI often leverages deep learning and neural networks to create new content.
Examples of industry-related Generative AI:
- Text Generation: Large language models like ChatGPT are examples of generative AI that produce coherent and contextually relevant text based on prompts or inputs.
- Art Generation: Users can create images, drawings, or other forms of art using generative AI algorithms trained on vast datasets of artistic styles.
- Music Composition: Generative AI models can compose original music in various genres by learning from existing compositions.
- Speech and Video Synthesis: AI-powered video synthesis can create videos, simulate human voices, or alter existing footage.
Distinctions between Non-generative and Generative AI
Understanding the distinctions between non-generative and generative AI is crucial because it defines their capabilities and potential use cases across industries. As we integrate AI technologies into our company’s operations, these definitions will guide implementation and usage strategies.
It is important to note that while these definitions provide valuable insight, our AI implementation approach will be further refined by considering additional factors such as compliance, data privacy, security, industry best practices, business objectives, and risk assessment.
Scope and Applicability
The scope and applicability section of the External AI Policy defines the boundaries and context within which the policy exists. The External AI Policy exists as a counterpart to the Internal AI Usage Policy.
AI technologies are being employed within our organization where deemed valuable and responsible. However, the policy serves to outline under which conditions AI-based solutions can be considered and clarifies the governance structures and oversight mechanisms put in place to ensure responsible AI implementation.
The aim is to create transparency to our clients, potential clients, and stakeholders regarding AI technologies and AI-related initiatives that are developed, procured, or used by our organization. It encompasses both non-generative and generative AI systems, considering their diverse applications and potential impact on our operations and stakeholders. The scope includes all ongoing and future AI projects, both internal and external, carried out on behalf of the organization. It extends to AI solutions developed in-house, as well as those integrated through partnerships with external vendors or third-party providers.
Parts of this policy have been generated using Generative AI; content has been fully revised.
Approval Process
Risk-based Approach
To ensure the integrity of the solutions we use, we rely on a risk assessment of each AI-based solution that is developed, procured, or used by our organization.
Each AI solution needs to have a risk assessment done by SPRING Group IT and SPRING Group Compliance and have one or more persons responsible for testing and listing use cases of the solution.
The risk assessment aims to classify and divide the different AI-based solutions into one of four categories following the Pyramid of Risks below:
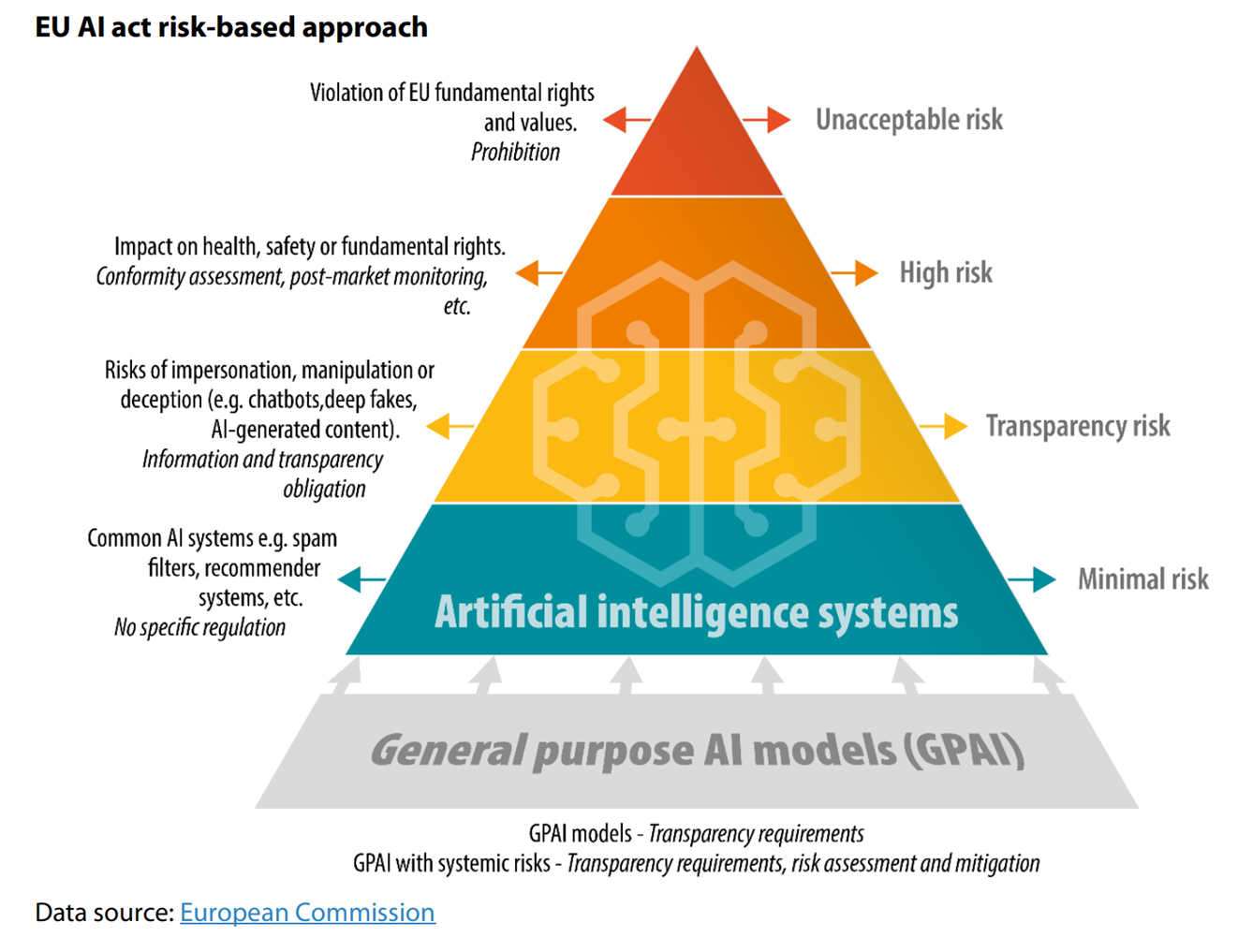
In this risk-based approach to the approval process, SPRING Group IT and SPRING Group Compliance will conduct risk assessments for each AI-based solution. The assessment will consider data privacy, security, integration, legal compliance, transparency, public knowledge, and supplier evaluation to ensure responsible and ethical AI implementation across the organization.
The risk assessments may change over time in case the AI-based solutions develop or change their terms as well as new information becoming public knowledge.
The categories entail the following usage limitations:
- Low and Minimal Risk
- AI-based solutions where both data handling and legal terms are fully under compliance or where the data handled or how it’s processed is considered to be non-critical.
- Can be used by all employees by following existing company rules and application guidelines.
- Limited Risk
- AI-based solutions with moderate risks, where the potential negative consequences can be managed through appropriate measures like general security measures and facilitation of awareness training/knowledge. These solutions may involve data processing but aren’t intended to handle sensitive, confidential, or business-critical information.
- Can be used by all employees by generic company rules and application guidelines..
- High Risk
- AI-based solutions that carry a potential substantial risk but where usage can be regulated to ensure data input and that potential generated content or access, and data handling can be strictly controlled.
- Can only be used by pre-approved employees and if a specific code of conduct is established and adhered to.
- Unacceptable Risk
- AI-based solutions that pose significant threats to data privacy, security, or violate legal regulations. Solutions that have a high potential for causing harm, discrimination, or severe negative consequences to individuals or society.
- All use of AI-based solutions in this category will be prohibited
Parts of this policy have been generated using Generative AI; content has been fully revised.
Data Security and Usage
Safeguarding the privacy and security of client data is key to our business and of greatest significance. As an organization that values trust and confidentiality, we adhere to a strict IT Policy and data processing agreements we have entered with clients and close suppliers, that serve as the primary foundation governing our handling of client data. This includes guidelines for data collection, security measures, storage, processing, and access, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations and best security practice.
When it comes to AI-based solutions, we recognize the need for enhanced data protection measures due to the nature of their operations. While we may utilize supplier or client data in AI models, we are committed to never sharing any client-owned material to public training pools or external repositories. Client data is treated with the utmost care and confidentiality, and we strictly control access to sensitive information, limiting it to authorized personnel only.
Furthermore, we prioritize transparency and open communication with our clients regarding AI usage and data handling. We believe in collaborating with our clients facilitating an understanding of how AI-based solutions work and how their data can contribute to improving our services. Client consent and trust remain fundamental to our AI implementation, and the client will always be informed upfront before usage. Depending on the intended usage of the solution, we will work with our client case by case to ensure screening and approval of the AI solution before use for production/commercial output.
AI Implementation – Steps, Roles, and Responsibilities
To ensure control over the AI implementation process, we have established a standardized process that employees must follow when utilizing AI tools or incorporating AI solutions into their projects, comprised of the following steps:
1. Pre-investigation of AI-based solution
2. Initial risk assessment
3. Production test
4. Compliance review
5. IT review
6. Final risk assessment / evaluation
AI Steering Committee
To ensure management and responsible usage of AI technology, we have established a group-wide Steering Committee comprised of members from SPRING Group IT, Compliance, and relevant stakeholders from every business unit. This committee is tasked with defining and maintaining our AI Code of Conduct and AI Policies. Through regular meetings and collaborative efforts, the AI Steering Committee plays a pivotal role in shaping SPRING Family’s AI strategy and fostering ethical AI practices within the entire group.
Transparency and open communication lie at the heart of our approach to AI. We encourage an ongoing dialogue with our clients to address any concerns or queries they may have about AI and its applications. Should our clients seek more information on any AI-related topic, we recommend engaging in a dialogue with their designated client contacts, who will assist in directing them to the appropriate sources of information.
In situations where urgent dialogue on AI becomes necessary, particularly in cases deemed business-critical or involving significant impacts on legal or ethical matters, the AI Steering Committee can be engaged for prompt action. The committee stands ready to address such situations and provide valuable insights, recommendations, and support to ensure the ethical and responsible deployment of AI across our organization.
Our AI Steering Committee is committed to upholding the highest standards of AI governance and promoting a culture of responsible AI use for the benefit of our clients and stakeholders.
WHAT WE DO
OUR WORK
ABOUT US
GET IN TOUCH →
AI Policy
In response to the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies and their increasing integra1on into our company's opera1ons, SPRING Family recognize the importance of establishing clear guidelines for the responsible and effective use of AI and has therefore implemented an Internal AI Usage Policy. The policy serves as a framework to promote ethical AI practices, protect data, ensure transparency, and mi1gate potential risks associated with both non-generative and generative AI within the en1re group.
As AI continues to evolve, the policy provides fundamental principles and considerations that will guide our approach to AI usage, ensuring alignment with our company values and objectives. It is designed to foster innovation while priori1zing the well-being of our clients, employees, and stakeholders.
As AI technology evolves and the business landscape changes, we will periodically review and update the AI Policy to stay in line with best practices and industry standards.
Definitions
Non-generative AI: Explanation and Examples
Non-generative AI, also known as traditional or narrow AI, refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to perform specific, predefined tasks within a limited scope. Unlike generative AI, these systems cannot create new content or generate novel information beyond their training data. Instead, they rely on predefined algorithms and patterns to execute tasks and provide solutions.
Examples of industry-related Non-generative AI:
- Image Recognition: Non-generative AI models can be trained to recognize objects, patterns, or faces in images, making them valuable tools across various applications.
- Recommendation Systems: E-commerce platforms often use non-generative AI to suggest products or content based on user behavior, purchase history, or preferences.
- Speech Recognition: Virtual assistants and voice-controlled devices utilize non-generative AI to convert spoken language into actionable commands.
Generative AI: Explanation and Examples
Generative AI, also referred to as creative AI, involves models capable of generating new content or data that was not present in the original training set. These systems are more versatile and can produce original output based on patterns learned during training. Generative AI often leverages deep learning and neural networks to create new content.
Examples of industry-related Generative AI:
- Text Generation: Large language models like ChatGPT are examples of generative AI that produce coherent and contextually relevant text based on prompts or inputs.
- Art Generation: Users can create images, drawings, or other forms of art using generative AI algorithms trained on vast datasets of artistic styles.
- Music Composition: Generative AI models can compose original music in various genres by learning from existing compositions.
- Speech and Video Synthesis: AI-powered video synthesis can create videos, simulate human voices, or alter existing footage.
Distinctions between Non-generative and Generative AI
Understanding the distinctions between non-generative and generative AI is crucial because it defines their capabilities and potential use cases across industries. As we integrate AI technologies into our company’s operations, these definitions will guide implementation and usage strategies.
It is important to note that while these definitions provide valuable insight, our AI implementation approach will be further refined by considering additional factors such as compliance, data privacy, security, industry best practices, business objectives, and risk assessment.
Scope and Applicability
The scope and applicability section of the External AI Policy defines the boundaries and context within which the policy exists. The External AI Policy exists as a counterpart to the Internal AI Usage Policy.
AI technologies are being employed within our organization where deemed valuable and responsible. However, the policy serves to outline under which conditions AI-based solutions can be considered and clarifies the governance structures and oversight mechanisms put in place to ensure responsible AI implementation.
The aim is to create transparency to our clients, potential clients, and stakeholders regarding AI technologies and AI-related initiatives that are developed, procured, or used by our organization. It encompasses both non-generative and generative AI systems, considering their diverse applications and potential impact on our operations and stakeholders. The scope includes all ongoing and future AI projects, both internal and external, carried out on behalf of the organization. It extends to AI solutions developed in-house, as well as those integrated through partnerships with external vendors or third-party providers.
Parts of this policy have been generated using Generative AI; content has been fully revised.
Approval Process
Risk-based Approach
To ensure the integrity of the solutions we use, we rely on a risk assessment of each AI-based solution that is developed, procured, or used by our organization.
Each AI solution needs to have a risk assessment done by SPRING Group IT and SPRING Group Compliance and have one or more persons responsible for testing and listing use cases of the solution.
The risk assessment aims to classify and divide the different AI-based solutions into one of four categories following the Pyramid of Risks below:

In this risk-based approach to the approval process, SPRING Group IT and SPRING Group Compliance will conduct risk assessments for each AI-based solution. The assessment will consider data privacy, security, integration, legal compliance, transparency, public knowledge, and supplier evaluation to ensure responsible and ethical AI implementation across the organization.
The risk assessments may change over time in case the AI-based solutions develop or change their terms as well as new information becoming public knowledge.
The categories entail the following usage limitations:
- Low and Minimal Risk
- AI-based solutions where both data handling and legal terms are fully under compliance or where the data handled or how it’s processed is considered to be non-critical.
- Can be used by all employees by following existing company rules and application guidelines.
- Limited Risk
- AI-based solutions with moderate risks, where the potential negative consequences can be managed through appropriate measures like general security measures and facilitation of awareness training/knowledge. These solutions may involve data processing but aren’t intended to handle sensitive, confidential, or business-critical information.
- Can be used by all employees by generic company rules and application guidelines..
- High Risk
- AI-based solutions that carry a potential substantial risk but where usage can be regulated to ensure data input and that potential generated content or access, and data handling can be strictly controlled.
- Can only be used by pre-approved employees and if a specific code of conduct is established and adhered to.
- Unacceptable Risk
- AI-based solutions that pose significant threats to data privacy, security, or violate legal regulations. Solutions that have a high potential for causing harm, discrimination, or severe negative consequences to individuals or society.
- All use of AI-based solutions in this category will be prohibited
Parts of this policy have been generated using Generative AI; content has been fully revised.
Data Security and Usage
Safeguarding the privacy and security of client data is key to our business and of greatest significance. As an organization that values trust and confidentiality, we adhere to a strict IT Policy and data processing agreements we have entered with clients and close suppliers, that serve as the primary foundation governing our handling of client data. This includes guidelines for data collection, security measures, storage, processing, and access, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations and best security practice.
When it comes to AI-based solutions, we recognize the need for enhanced data protection measures due to the nature of their operations. While we may utilize supplier or client data in AI models, we are committed to never sharing any client-owned material to public training pools or external repositories. Client data is treated with the utmost care and confidentiality, and we strictly control access to sensitive information, limiting it to authorized personnel only.
Furthermore, we prioritize transparency and open communication with our clients regarding AI usage and data handling. We believe in collaborating with our clients facilitating an understanding of how AI-based solutions work and how their data can contribute to improving our services. Client consent and trust remain fundamental to our AI implementation, and the client will always be informed upfront before usage. Depending on the intended usage of the solution, we will work with our client case by case to ensure screening and approval of the AI solution before use for production/commercial output.
AI Implementation – Steps, Roles, and Responsibilities
To ensure control over the AI implementation process, we have established a standardized process that employees must follow when utilizing AI tools or incorporating AI solutions into their projects, comprised of the following steps:
1. Pre-investigation of AI-based solution
2. Initial risk assessment
3. Production test
4. Compliance review
5. IT review
6. Final risk assessment / evaluation
AI Steering Committee
To ensure management and responsible usage of AI technology, we have established a group-wide Steering Committee comprised of members from SPRING Group IT, Compliance, and relevant stakeholders from every business unit. This committee is tasked with defining and maintaining our AI Code of Conduct and AI Policies. Through regular meetings and collaborative efforts, the AI Steering Committee plays a pivotal role in shaping SPRING Family’s AI strategy and fostering ethical AI practices within the entire group.
Transparency and open communication lie at the heart of our approach to AI. We encourage an ongoing dialogue with our clients to address any concerns or queries they may have about AI and its applications. Should our clients seek more information on any AI-related topic, we recommend engaging in a dialogue with their designated client contacts, who will assist in directing them to the appropriate sources of information.
In situations where urgent dialogue on AI becomes necessary, particularly in cases deemed business-critical or involving significant impacts on legal or ethical matters, the AI Steering Committee can be engaged for prompt action. The committee stands ready to address such situations and provide valuable insights, recommendations, and support to ensure the ethical and responsible deployment of AI across our organization.
Our AI Steering Committee is committed to upholding the highest standards of AI governance and promoting a culture of responsible AI use for the benefit of our clients and stakeholders.
WHAT WE DO
OUR WORK
ABOUT US
GET IN TOUCH →
AI Policy
In response to the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies and their increasing integra1on into our company's opera1ons, SPRING Family recognize the importance of establishing clear guidelines for the responsible and effective use of AI and has therefore implemented an Internal AI Usage Policy. The policy serves as a framework to promote ethical AI practices, protect data, ensure transparency, and mi1gate potential risks associated with both non-generative and generative AI within the en1re group.
As AI continues to evolve, the policy provides fundamental principles and considerations that will guide our approach to AI usage, ensuring alignment with our company values and objectives. It is designed to foster innovation while priori1zing the well-being of our clients, employees, and stakeholders.
As AI technology evolves and the business landscape changes, we will periodically review and update the AI Policy to stay in line with best practices and industry standards.
Definitions
Non-generative AI: Explanation and Examples
Non-generative AI, also known as traditional or narrow AI, refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to perform specific, predefined tasks within a limited scope. Unlike generative AI, these systems cannot create new content or generate novel information beyond their training data. Instead, they rely on predefined algorithms and patterns to execute tasks and provide solutions.
Examples of industry-related Non-generative AI:
- Image Recognition: Non-generative AI models can be trained to recognize objects, patterns, or faces in images, making them valuable tools across various applications.
- Recommendation Systems: E-commerce platforms often use non-generative AI to suggest products or content based on user behavior, purchase history, or preferences.
- Speech Recognition: Virtual assistants and voice-controlled devices utilize non-generative AI to convert spoken language into actionable commands.
Generative AI: Explanation and Examples
Generative AI, also referred to as creative AI, involves models capable of generating new content or data that was not present in the original training set. These systems are more versatile and can produce original output based on patterns learned during training. Generative AI often leverages deep learning and neural networks to create new content.
Examples of industry-related Generative AI:
- Text Generation: Large language models like ChatGPT are examples of generative AI that produce coherent and contextually relevant text based on prompts or inputs.
- Art Generation: Users can create images, drawings, or other forms of art using generative AI algorithms trained on vast datasets of artistic styles.
- Music Composition: Generative AI models can compose original music in various genres by learning from existing compositions.
- Speech and Video Synthesis: AI-powered video synthesis can create videos, simulate human voices, or alter existing footage.
Distinctions between Non-generative and Generative AI
Understanding the distinctions between non-generative and generative AI is crucial because it defines their capabilities and potential use cases across industries. As we integrate AI technologies into our company’s operations, these definitions will guide implementation and usage strategies.
It is important to note that while these definitions provide valuable insight, our AI implementation approach will be further refined by considering additional factors such as compliance, data privacy, security, industry best practices, business objectives, and risk assessment.
Scope and Applicability
The scope and applicability section of the External AI Policy defines the boundaries and context within which the policy exists. The External AI Policy exists as a counterpart to the Internal AI Usage Policy.
AI technologies are being employed within our organization where deemed valuable and responsible. However, the policy serves to outline under which conditions AI-based solutions can be considered and clarifies the governance structures and oversight mechanisms put in place to ensure responsible AI implementation.
The aim is to create transparency to our clients, potential clients, and stakeholders regarding AI technologies and AI-related initiatives that are developed, procured, or used by our organization. It encompasses both non-generative and generative AI systems, considering their diverse applications and potential impact on our operations and stakeholders. The scope includes all ongoing and future AI projects, both internal and external, carried out on behalf of the organization. It extends to AI solutions developed in-house, as well as those integrated through partnerships with external vendors or third-party providers.
Parts of this policy have been generated using Generative AI; content has been fully revised.
Approval Process
Risk-based Approach
To ensure the integrity of the solutions we use, we rely on a risk assessment of each AI-based solution that is developed, procured, or used by our organization.
Each AI solution needs to have a risk assessment done by SPRING Group IT and SPRING Group Compliance and have one or more persons responsible for testing and listing use cases of the solution.
The risk assessment aims to classify and divide the different AI-based solutions into one of four categories following the Pyramid of Risks below:

In this risk-based approach to the approval process, SPRING Group IT and SPRING Group Compliance will conduct risk assessments for each AI-based solution. The assessment will consider data privacy, security, integration, legal compliance, transparency, public knowledge, and supplier evaluation to ensure responsible and ethical AI implementation across the organization.
The risk assessments may change over time in case the AI-based solutions develop or change their terms as well as new information becoming public knowledge.
The categories entail the following usage limitations:
- Low and Minimal Risk
- AI-based solutions where both data handling and legal terms are fully under compliance or where the data handled or how it’s processed is considered to be non-critical.
- Can be used by all employees by following existing company rules and application guidelines.
- Limited Risk
- AI-based solutions with moderate risks, where the potential negative consequences can be managed through appropriate measures like general security measures and facilitation of awareness training/knowledge. These solutions may involve data processing but aren’t intended to handle sensitive, confidential, or business-critical information.
- Can be used by all employees by generic company rules and application guidelines..
- High Risk
- AI-based solutions that carry a potential substantial risk but where usage can be regulated to ensure data input and that potential generated content or access, and data handling can be strictly controlled.
- Can only be used by pre-approved employees and if a specific code of conduct is established and adhered to.
- Unacceptable Risk
- AI-based solutions that pose significant threats to data privacy, security, or violate legal regulations. Solutions that have a high potential for causing harm, discrimination, or severe negative consequences to individuals or society.
- All use of AI-based solutions in this category will be prohibited
Parts of this policy have been generated using Generative AI; content has been fully revised.
Data Security and Usage
Safeguarding the privacy and security of client data is key to our business and of greatest significance. As an organization that values trust and confidentiality, we adhere to a strict IT Policy and data processing agreements we have entered with clients and close suppliers, that serve as the primary foundation governing our handling of client data. This includes guidelines for data collection, security measures, storage, processing, and access, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations and best security practice.
When it comes to AI-based solutions, we recognize the need for enhanced data protection measures due to the nature of their operations. While we may utilize supplier or client data in AI models, we are committed to never sharing any client-owned material to public training pools or external repositories. Client data is treated with the utmost care and confidentiality, and we strictly control access to sensitive information, limiting it to authorized personnel only.
Furthermore, we prioritize transparency and open communication with our clients regarding AI usage and data handling. We believe in collaborating with our clients facilitating an understanding of how AI-based solutions work and how their data can contribute to improving our services. Client consent and trust remain fundamental to our AI implementation, and the client will always be informed upfront before usage. Depending on the intended usage of the solution, we will work with our client case by case to ensure screening and approval of the AI solution before use for production/commercial output.
AI Implementation – Steps, Roles, and Responsibilities
To ensure control over the AI implementation process, we have established a standardized process that employees must follow when utilizing AI tools or incorporating AI solutions into their projects, comprised of the following steps:
1. Pre-investigation of AI-based solution
2. Initial risk assessment
3. Production test
4. Compliance review
5. IT review
6. Final risk assessment / evaluation
AI Steering Committee
To ensure management and responsible usage of AI technology, we have established a group-wide Steering Committee comprised of members from SPRING Group IT, Compliance, and relevant stakeholders from every business unit. This committee is tasked with defining and maintaining our AI Code of Conduct and AI Policies. Through regular meetings and collaborative efforts, the AI Steering Committee plays a pivotal role in shaping SPRING Family’s AI strategy and fostering ethical AI practices within the entire group.
Transparency and open communication lie at the heart of our approach to AI. We encourage an ongoing dialogue with our clients to address any concerns or queries they may have about AI and its applications. Should our clients seek more information on any AI-related topic, we recommend engaging in a dialogue with their designated client contacts, who will assist in directing them to the appropriate sources of information.
In situations where urgent dialogue on AI becomes necessary, particularly in cases deemed business-critical or involving significant impacts on legal or ethical matters, the AI Steering Committee can be engaged for prompt action. The committee stands ready to address such situations and provide valuable insights, recommendations, and support to ensure the ethical and responsible deployment of AI across our organization.
Our AI Steering Committee is committed to upholding the highest standards of AI governance and promoting a culture of responsible AI use for the benefit of our clients and stakeholders.
General enquiries
hello@spring-cc.com
Copyright 2025 Spring CC. All Rights Reserved.